
In search of relief for sore muscles and aching joints?
Our Joint and Muscle Cream is here to help! Enriched with natural ingredients, including Green Lipped Mussel oil and Arnica, it's the ideal solution for the active individual. Welcome soothing comfort and bid farewell to sore muscles and joints, while ensuring your skin remains vibrant and well-nourished.
Recent posts
-

-
 Joints and Muscle Creams for Athletes and Active PeopleBy Ben Winters
Joints and Muscle Creams for Athletes and Active PeopleBy Ben Winters -
 Muscle Warm-Up and Cool-Down, Injury Prevention for RunnersBy Ben Winters
Muscle Warm-Up and Cool-Down, Injury Prevention for RunnersBy Ben Winters

About the Author
Guiding Lifespan's to the best quality joint supplements, Ben Winters infuses his dedication to natural wellness into our Green Lipped Mussel Cream. With a keen eye on sustainable practices and innovative product formulation, Ben guarantees the highest quality of every batch. Tailored for those with an energetic lifestyle, this cream stands as a reflection of Ben's devotion to superior quality and efficiency, providing fast relief for joint and muscle discomfort. Immerse yourself in a blend of nature's finest and cutting-edge science with each application
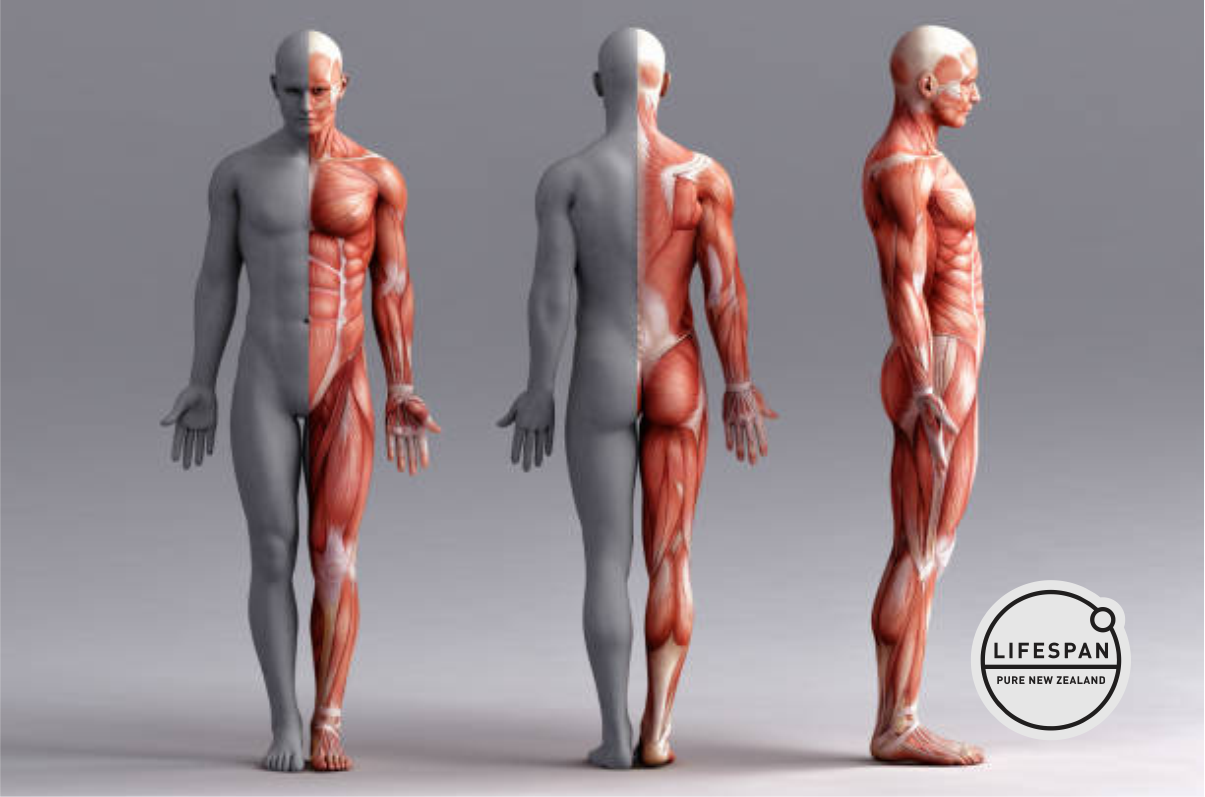
Muscles Revealed: What Are Their Roles in Our Bodies?
By Ben Winters
Have you ever stopped to think about what keeps you moving every day?
It's your muscles – they are essential for practically everything you do.
From blinking your eyes to running a marathon, our muscles are making this possible.
Your body boasts over 600 muscles, each playing a unique role. But did you know there are different types of muscles?
There are three main types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles and each type has a special function:
Skeletal muscles are attached to your bones and are in charge of all your movements. When you decide to walk, dance, or lift something, it's your skeletal muscles at work.
Smooth muscles are the behind-the-scenes workers. You'll find them in places like your stomach and blood vessels, doing their jobs without you even realising it. They help digest your food and regulate blood flow, among other things.
Cardiac muscle is your heart's muscle. It works tirelessly, contracting and relaxing to pump blood throughout your body, keeping you alive and well.
Understanding Muscle Anatomy
Let's take a closer look at what makes up a muscle. Imagine your muscles as incredibly intricate machines, each part working together to create movement. They're not just random bundles of fibers – there's a whole system in play!
First off, think of muscle fibers. These are the individual cells that make up a muscle, and they're long and slender – kind of like strings in a rope. When a bunch of these fibers come together, they form what we call a 'fascicle.' Now, imagine several fascicles bundled together, and voilà, you have a whole muscle!
But muscles don't work alone. They're connected to your bones by tendons.
Tendons are like tough, flexible cords that pull on your bones when your muscles contract, causing you to move. It's a teamwork between muscles and bones that lets you perform everything from lifting a cup of coffee to doing a backflip.
Now, here's where it gets really interesting. Inside each muscle fiber, there are even smaller structures called myofilaments. These are made up of proteins – actin and myosin. Think of them as tiny molecular motors. When you decide to move, these little guys slide past each other, causing the muscle to contract. This process is fueled by energy from the food you eat, transformed into movement by these microscopic wonders.
Every time you take a step, write a text, or wave to a friend, remember: it's a complex symphony of fibers, fascicles, tendons, and proteins working in perfect harmony.

Muscle Contraction and Movement
Have you ever wondered what happens inside your body when you decide to move? The process of muscle contraction and the role of the nervous system in this dance of movement is nothing short of fascinating.
When you decide to take a step or lift your arm, a complex and coordinated action takes place. It starts in your brain, which sends electrical signals through the nervous system to the muscles. This is where the real magic happens. Inside each muscle, particularly skeletal muscles, are those tiny fibers we talked about earlier. These fibers contain even smaller components called actin and myosin.
During a muscle contraction, these actin and myosin filaments slide past each other, shortening the muscle fiber. This is what pulls on the tendon and, subsequently, moves the bone. This sliding mechanism is powered by ATP, the energy currency of your cells, which is derived from the food you eat.
Not all muscle movements are under your direct control.
Think about your heartbeat or the way your stomach digests food. These movements are controlled by involuntary muscles (cardiac and smooth muscles) that work automatically, guided by their own intrinsic systems and signals from your body.
The coordination and timing of muscle contractions are crucial for smooth, purposeful movements. Your brain and nervous system work tirelessly to ensure that muscles contract and relax in a harmonious manner, whether you're running a marathon or simply typing a text message.
And it's not just about moving. Muscle contractions play a key role in maintaining posture and stabilizing your joints. Even when you're sitting still, your muscles are subtly contracting to keep you upright and balanced.
Muscle Health and Maintenance
Maintaining the health of your muscles is key to a vibrant and active life. Whether you're an athlete, a weekend warrior, or just looking to stay mobile and pain-free, understanding how to care for your muscles is essential.
Exercise: Your Muscles' Best Friend Regular exercise is vital for keeping your muscles strong and flexible. It doesn't have to be intense gym sessions; even simple activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can significantly benefit your muscle health. Exercise helps improve muscle strength, enhances coordination, and increases endurance. Plus, it's great for your overall health too!
Nutrition and Hydration: Fuel and Water for Your Muscles Just like any machine, your muscles need the right fuel to function optimally. A balanced diet rich in proteins, carbohydrates, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals is crucial. Proteins are especially important as they are the building blocks of muscle tissue. Don't forget about hydration! Water plays a key role in muscle performance and recovery, so make sure you're drinking enough throughout the day.
Rest is just as important as exercise. Your muscles need time to repair and strengthen, especially after intense activities.
Ensure you're getting enough sleep and giving yourself rest days between heavy workouts. This is when your muscles do most of their healing and growing.
Muscles do more than just help us move; they play a crucial role in our overall health and well-being.
Understanding these roles can help you appreciate the importance of maintaining muscle health as part of a holistic approach to wellness.
Your muscles are significant players in your metabolism.
They burn calories not only when you're active but also at rest. Muscle tissue is more metabolically active than fat, meaning the more muscle you have, the higher your resting metabolic rate. This is why building muscle mass can be a key component in managing weight and increasing energy levels.
Muscles also help regulate your body temperature.
When you're cold, your muscles generate heat by shivering. This involuntary contraction of muscles helps maintain a stable body temperature in colder environments.
Beyond movement and metabolism, muscles provide support and protection for your internal organs.
Your abdominal muscles, for instance, help support your spine and internal organs, while your pelvic muscles are crucial for bladder control and childbirth.
There's also a strong link between muscle health and mental health.
Regular physical activity, which builds and maintains muscle, is known to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. Exercise releases endorphins, often referred to as 'feel-good hormones', which can improve mood and decrease feelings of stress and anxiety.
Maintaining strong muscles can contribute to overall health and longevity. Strong muscles can reduce the risk of falls and injuries, particularly in older adults, and contribute to better posture, balance, and flexibility.
Muscles do much more than move us; they are integral to our metabolic health, body temperature regulation, physical protection, mental well-being, and overall longevity. So, when you think about muscle health, remember it's not just about looking good – it's about keeping your entire body and mind in top shape.



